Cloud Microphysics VAP Evaluation Data Available for LASIC Field Campaign
Published: 20 January 2020
Cloud microphysical properties affect cloud radiative heating, precipitation formation, and aerosol-cloud interactions, among other important atmospheric processes. The first field campaign data are now available from a value-added product (VAP) that builds upon the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) user facility’s historical Continuous Baseline Microphysical Retrieval (MICROBASE) VAP.
The Improved MICROBASE Product with Uncertainties (MICROBASEKAPLUS) provides continuous, high time resolution profiles of cloud microphysical properties such as the liquid/ice water content and liquid/ice effective radius. The VAP was primarily developed for estimating radiative heating rate profiles, but scientists can use it for diverse applications, including evaluation of model cloud parameterizations, process studies of precipitation formation, and cloud particle phase partitioning.
Currently, MICROBASEKAPLUS evaluation data are available for the 2016‒2017 Layered Atlantic Smoke Interactions with Clouds (LASIC) field campaign on Ascension Island in the South Atlantic Ocean.
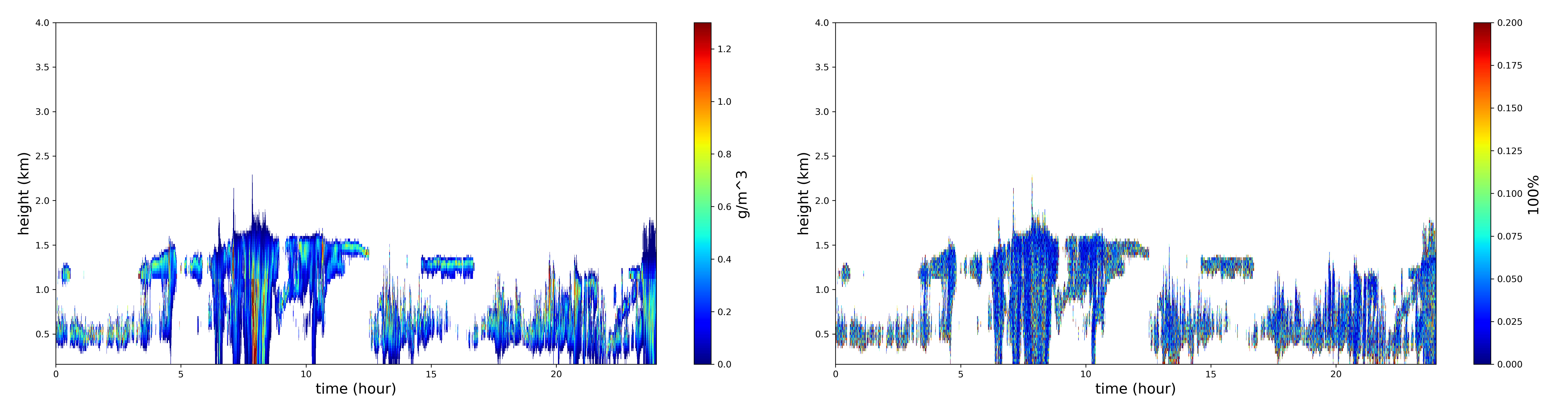
MICROBASEKAPLUS uses parameterizations identical to those used by MICROBASE for determining the liquid/ice water content and liquid/ice effective radius. However, MICROBASEKAPLUS adds uncertainties to these quantities using a perturbation method first applied through the Atmospheric System Research (ASR) Quantifying Uncertainty in Cloud Retrievals (QUICR) science focus group (Zhao et al. 2014).
To determine the cloud microphysical properties, MICROBASEKAPLUS uses a combination of data from the Active Remote Sensing of Clouds (ARSCL) product using Ka-Band ARM Zenith Radars (KAZR-ARSCL), the Interpolated Sounding (INTERPOLATEDSONDE) VAP, and the Microwave Radiometer Retrievals (MWRRET) VAP. The MICROBASEKAPLUS product is archived as daily data files, with a time resolution of 4 seconds and vertical resolution of 30 meters to 18,010 meters, which is consistent with the KAZR-ARSCL data resolutions.
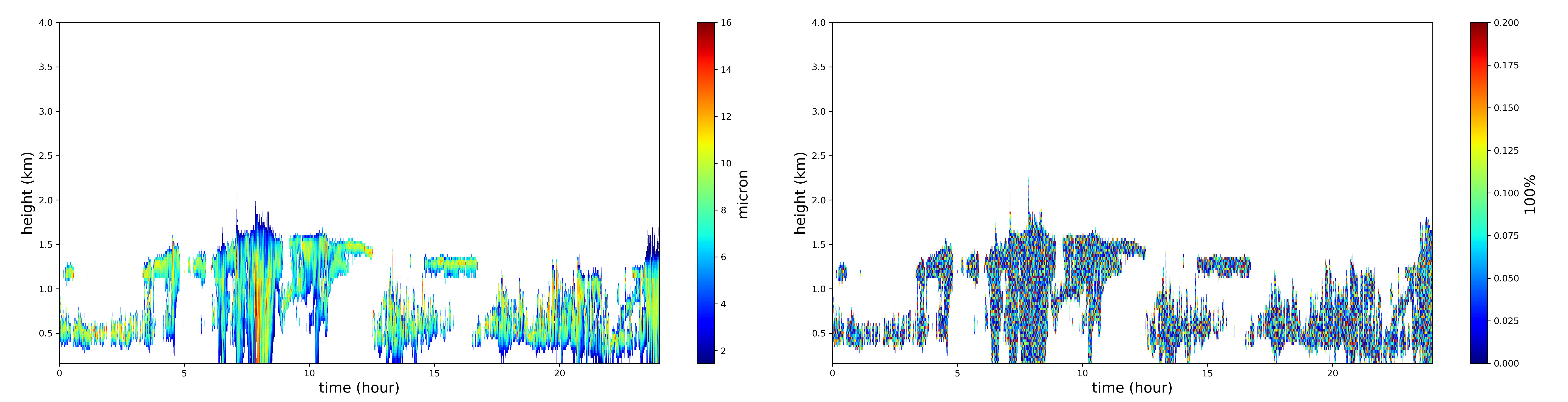
Evaluation data are available for LASIC from August 1, 2016, through September 30, 2016, and from August 1, 2017, through September 30, 2017. Scientists can use these data now.
Ongoing work aims to use MICROBASEKAPLUS within the ARM Operational Ground-Based Retrieval Evaluation for Clouds (OGRE-CLOUDS) framework, evaluating improvements to cloud microphysics retrievals through radiative closure studies, comparisons to in situ measurements, and instrument simulator comparisons. Through this process, the development team anticipates a continuous improvement of the cloud microphysical estimates.
More information on MICROBASEKAPLUS is available on the VAP web page. During this evaluation period, please send any product-related comments and suggestions to Michael Jensen, VAP translator, or Meng Wang, data product developer. Such feedback will assist in improving the product before its full release.
Users can access the data set from the ARM Data Center. (Go here to create an account to download the data.)
To cite the MICROBASEKAPLUS data, please use doi:10.5439/1438196.
Reference: Zhao C, S Xie, X Chen, MP Jensen, and M Dunn. 2014. “Quantifying uncertainties of cloud microphysical property retrievals with a perturbation method.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 119(9), 10.1002/2013jd021112.
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















