Aerosol size distribution properties associated with cold-air outbreaks in the Norwegian Arctic
Submitter
Russell, Lynn M
— Scripps Institution of Oceanography
Area of Research
Aerosol Properties
Journal Reference
Williams A, J Dedrick, L Russell, F Tornow, I Silber, A Fridlind, B Swanson, P DeMott, P Zieger, and R Krejci. 2024. "Aerosol size distribution properties associated with cold-air outbreaks in the Norwegian Arctic." 24(20), 10.5194/acp-24-11791-2024.
Science
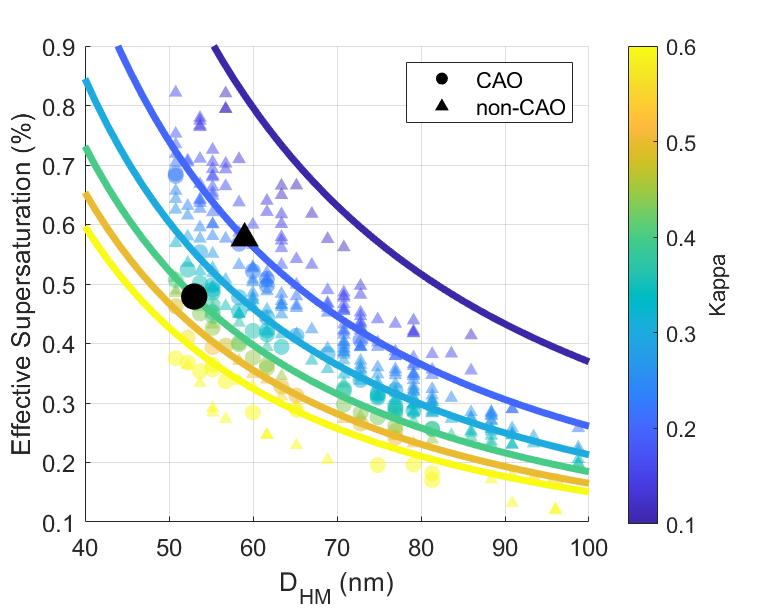
Scatter plot of effective supersaturation against DHM colored by hygroscopicity (κ). Measurements during CAO events are represented by the circles, and measurements during non-CAO conditions are represented by the triangles. Overlaid are lines of constant hygroscopicity (κ) at intervals of 0.1 between 0.1 and 0.6, as described by the relationship between supersaturation, diameter, and κ given in Petters and Kreidenweis (2007). In black are the points corresponding to the median DHM and median hygroscopicity (κ) at 50 nm for CAO events and non-CAO conditions. Measurements for DHM < 50 nm are omitted since there are no HTDMA-derived κ measurements below this size. Image from journal.
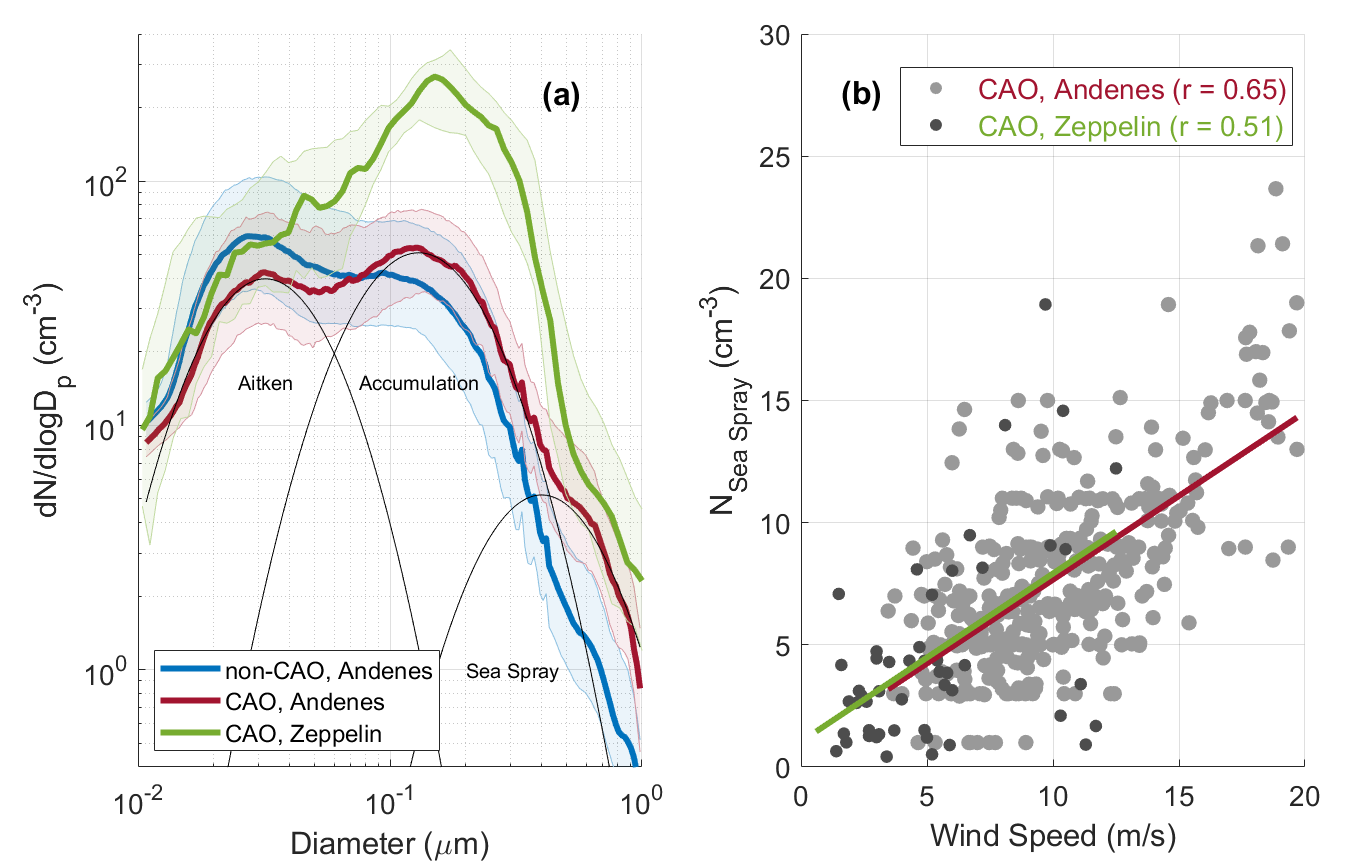
(a) Median particle number size distributions (thick solid lines) with 25th and 75th percentiles (shaded regions) for non-CAO conditions at Andenes (blue), CAO events at Andenes (red), and CAO event back trajectories at Zeppelin Observatory (green). The median CAO distribution at Andenes is overlaid with the Aitken, accumulation, and sea spray modes (thin black lines). (b) Scatter plots of the sea-spray-mode number concentration against measured wind speed. Points are 2 h means during CAO events at Andenes (light gray points) or when CAO event back trajectories pass near Zeppelin Observatory (dark gray points) and are overlaid with the corresponding regression line for Andenes and Zeppelin Observatory (red and green lines, respectively). Image from journal.
We determine the characteristics of the aerosol size distribution associated with cold-air outbreaks over the Norwegian Sea, using observational measurements taken at Andenes, Norway and approximately 1000 km upwind at Zeppelin Observatory in Svalbard during ARM's Cold-Air Outbreaks in the Marine Boundary Layer Experiment (COMBLE).
Impact
Aerosol particles serving as cloud condensation and ice nuclei contribute to key cloud processes associated with cold-air outbreak (CAO) events but are poorly constrained in climate models due to sparse observations. The distinct aerosol properties we find associated with CAO events provide important insights for evaluating CAO aerosol-cloud interaction processes in models.
Summary
We retrieve aerosol number size distribution modes from measurements at Andenes, Norway, during ARM's Cold-Air Outbreaks in the Marine Boundary Layer Experiment (COMBLE) and at Zeppelin Observatory, approximately 1000 km upwind from Andenes at Svalbard. During CAO events at Andenes, the sea spray mode number concentration is correlated with strong over-ocean winds with a mean of 8±4 cm−3 that is 71% higher than during non-CAO conditions. Additionally, during CAO events at Andenes, the mean Hoppel minimum diameter is 6 nm smaller than during non-CAO conditions, though the estimated cloud supersaturation is lower due to higher particle hygroscopicity. The mean number concentration of particles that likely activated to cloud droplets is 109±61 cm−3 with no statistically significant difference from the non-CAO mean of 99±66 cm−3. For CAO trajectories between Zeppelin Observatory and Andenes, the upwind-to-downwind change in particle number concentration is the largest for the accumulation mode with a mean decrease of 93±95 cm−3, likely primarily attributable to removal by precipitation.
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















