Aerosol-boundary-layer interaction modulated entrainment process
Submitter
Su, Tianning — Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Li, Zhanqing — University of Maryland
Area of Research
Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Vertical Structures
Journal Reference
Su T, Z Li, Y Zheng, T Wu, H Wu, and J Guo. 2022. "Aerosol-boundary layer interaction modulated entrainment process." 5(1), 64, 10.1038/s41612-022-00283-1.
Science
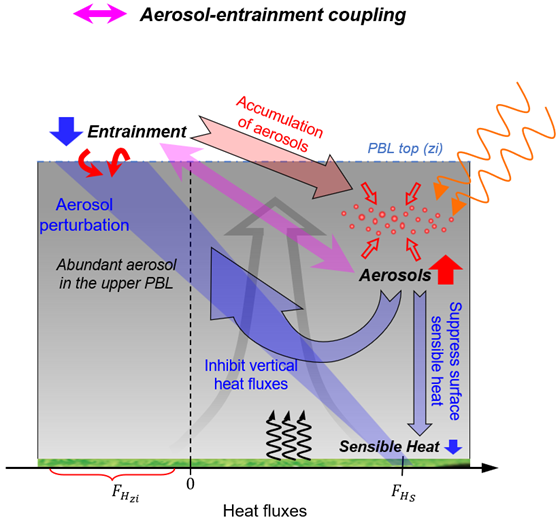
Figure 1. A schematic diagram describing the aerosol-entrainment coupling. Under the polluted condition, aerosol can suppress the sensible heat and vertical heat fluxes (blue arrows). The suppressed entrainment process can facilitate the accumulation of aerosols over the upper PBL (red arrows). Due to these interactions, the entrainment and aerosols are coupled here (marked as the pink double arrow). From journal.
This study proposes a new mechanism of aerosol-entrainment coupling that demonstrates the interactions between aerosols and the entrainment process and highlights the importance of accounting for this effect in numerical model simulations of the boundary layer.
Impact
The findings provide a new understanding of the role of aerosols in boundary-layer entrainment, which is critical for improving numerical model simulations of the boundary layer and predicting air pollution dispersion. The proposed mechanism of aerosol-entrainment coupling can advance our understanding of aerosol climate effects.
Summary
We investigated the impact of aerosols on the entrainment process using comprehensive field observations. Our findings indicate that high levels of aerosol loading can significantly suppress entrainment rates, which breaks the conventional linear relationship between sensible heat fluxes and entrainment fluxes. We propose a new mechanism of aerosol-entrainment coupling, which alters heat fluxes and can inhibit boundary-layer development, leading to a great sensitivity of observed entrainment rates to aerosols that is not accounted for in traditional model calculations. Our study highlights the impacts of aerosols on the dynamic framework of the boundary layer, and suggests the need for revised parameterizations in numerical models to account for the strong interaction between aerosols and the entrainment process.
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















