Mixing state of black-carbon particles from wildfires remains dynamic throughout their lifetime
Submitter
Sedlacek, Arthur J
— Brookhaven National Laboratory
Lewis, Ernie R.
— Brookhaven National Laboratory
Area of Research
Aerosol Processes
Journal Reference
Sedlacek A, E Lewis, T Onasch, P Zuidema, J Redemann, D Jaffe, and L Kleinman. 2022. "Using the Black Carbon Particle Mixing State to Characterize the Lifecycle of Biomass Burning Aerosols." Environmental Science & Technology, 56(20), 10.1021/acs.est.2c03851.
Science
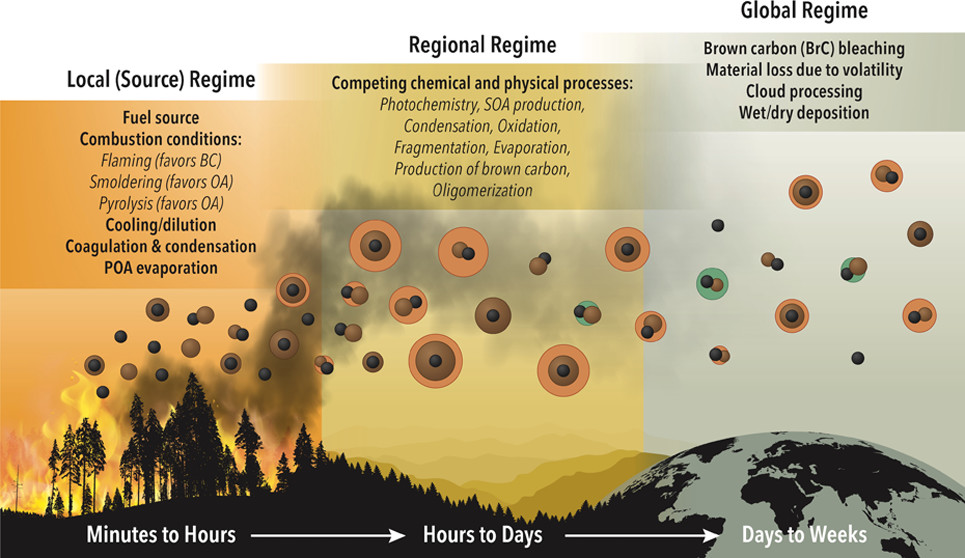
Figure 1. In the local (or source) regime, aerosol properties are controlled by source fuel, combustion conditions, cooling and dilution, and competition between coagulation and condensation. As these aerosols age in the atmosphere, particle properties are driven more by chemical processes, including oxidation, photochemistry, SOA production, fragmentation, and oligomerization. Continued aging opens new processing channels that impact optical properties such as brown-carbon bleaching, material loss due to volatility, cloud processing, and wet/dry deposition. From journal.
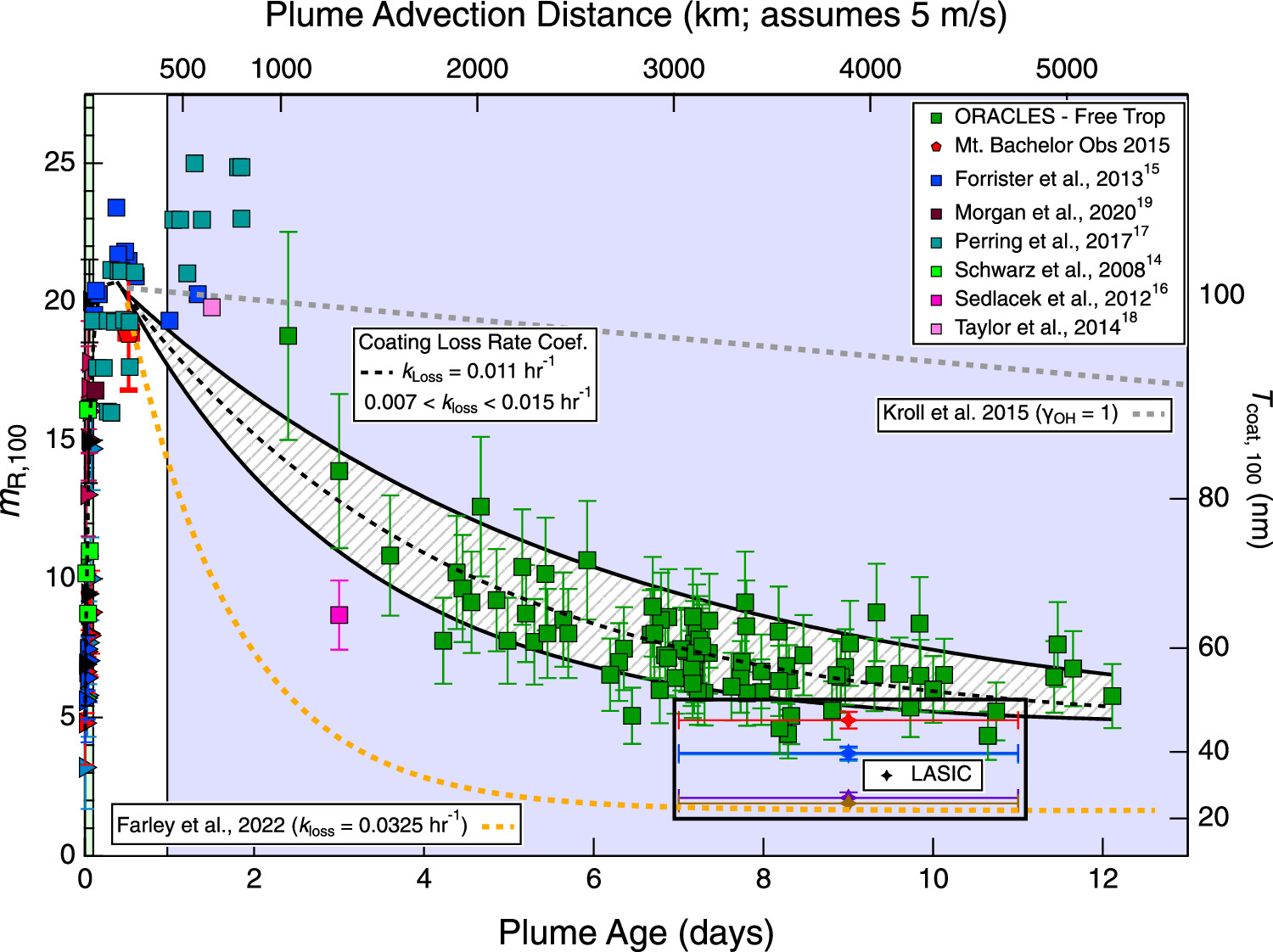
Figure 2. Mass ratio of coating to black carbon (BC) for BC-containing particles from biomass burns with BC mass-equivalent diameter of 100 nm, mR,100, (left axis) and corresponding coating thickness, Tcoat, (right axis) as functions of plume age, from field measurements. Also shown are squalene mass loss for a γOH of 1 from Kroll et al. from lab measurements and mass loss of OA from Farley et al. from field measurements. Hashed region captures loss rate constants 50% of nominal kloss. The dominant process in the BB−BC mixing state life cycle is the loss of coating. From journal.
The evolution of the mixing state of black carbon-containing particles formed by wildfires is characterized using field measurements. These particles rapidly (within an hour or so) attain a thick coating of organic material, but the majority of the lifetime of these particles is characterized by a slow loss of this coating.
Impact
Most model treatments of biomass burn aerosol are based on measurements in the near-field region where the particles have thick coatings, yet the vast majority of the lifetime of these particles is characterized by loss of coating and needs to be taken into account.
Summary
The life cycle of black carbon (BC)-containing particles from biomass burns is examined using aircraft and surface observations of the BC mixing state for plume ages from ∼15 min to 10 days. Because BC is nonvolatile and chemically inert, changes in the mixing state of BC-containing particles are driven solely by changes in particle coating, which is mainly secondary organic aerosol (SOA). The coating mass initially increases rapidly (kgrowth = 0.84 h−1), then remains relatively constant for 1−2 days as plume dilution no longer supports further growth, then decreases slowly until only ∼30% of the maximum coating mass remains after 10 days (kloss = 0.011 h−1). The mass ratio of coating to core for a BC-containing particle with a 100 nm mass-equivalent diameter BC core reaches a maximum of ∼20 after a few hours and drops to ∼5 after 10 days of aging. The initial increase in coating mass can be used to determine SOA formation rates. The slow loss of coating material, not captured in global models, comprises the dominant fraction of the life cycle of these particles.
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















