Satellite-Aligned Version of Ka-Band ARM Zenith Radar Product Now Available
Published: 3 August 2022
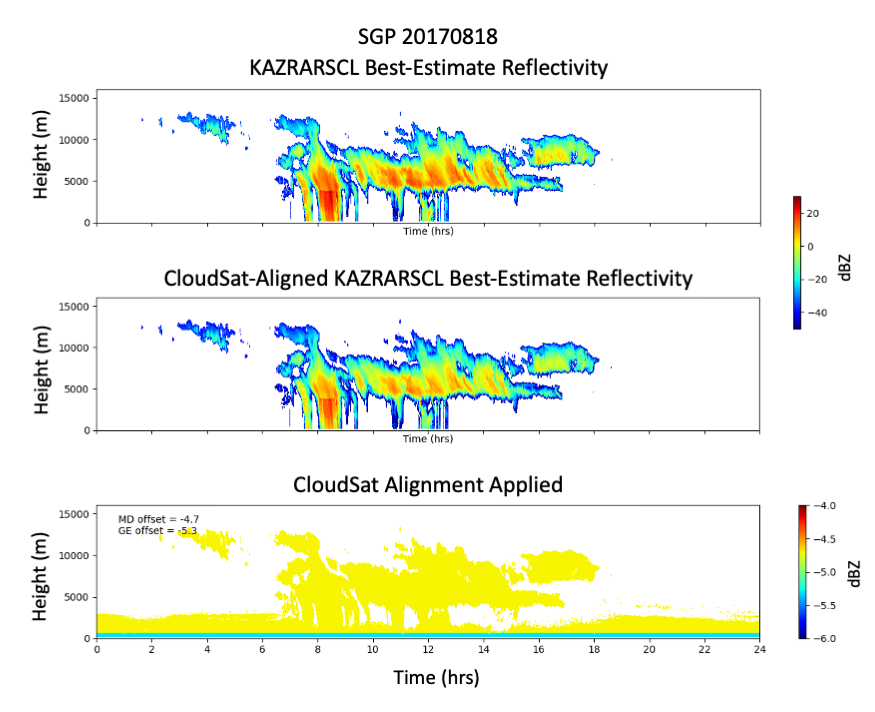
The Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) user facility has released a satellite-aligned version of its widely used Ka-Band ARM Zenith Radar Active Remote Sensing of CLouds (KAZRARSCL) product.
The new value-added product (VAP) aligns radar reflectivities from KAZRARSCL with those from the well-characterized Cloud Profiling Radar operating on NASA’s CloudSat satellite.
Because reliable external calibration sources are not readily available for the KAZRs, the alignment with CloudSat-based measurements provides an additional measure of confidence in the KAZRARSCL reflectivity observations.
The KAZRARSCL-CLOUDSAT VAP applies a statistical CloudSat-derived offset to the KAZRARSCL reflectivity and best-estimate reflectivity fields. The remaining KAZRARSCL product fields are not modified but are passed through to the resulting product.
Kollias et al. (2019) describes the algorithm used to determine the reflectivity offsets. It is important to note that the approach used is not necessarily instantaneously representative of the reflectivity offset and/or its change over time for a singular event in the record.
The new product is available only for periods for which both the KAZRARSCL VAP and monthly statistically derived CloudSat-based reflectivity offsets are available.
Users can access the new product for the following ARM sites and periods:
- the North Slope of Alaska atmospheric observatory for most months from March 2012 through June 2017
- the Southern Great Plains atmospheric observatory for most months from March 2012 through August 2017
- Oliktok Point, Alaska, from November 2015 through November 2017
- McMurdo Station, Antarctica, from April to June 2016 and August through December 2016 as part of the ARM West Antarctic Radiation Experiment (AWARE).
Scientists can begin using the CloudSat-aligned KAZRARSCL data now. More information about KAZRARSCL-CLOUDSAT is available on the VAP web page.
For questions or to report data problems, please contact developer/radar data mentor Karen Johnson or ARM translator Scott Giangrande.
Access the data in the ARM Data Center. (Go here to create an account to download the data.)
Data can be referenced as doi:10.5439/1728666.
Reference: Kollias P, B Puigdomènech Treserras, and A Protat. 2019. “Calibration of the 2007–2017 record of Atmospheric Radiation Measurements cloud radar observations using CloudSat.” Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 12(9), https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-12-4949-2019.
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















