New Lifting Condensation Level Height VAP Available
Published: 22 June 2020
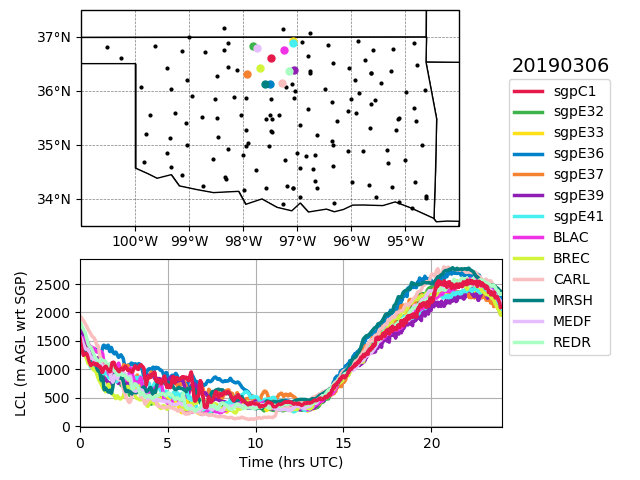
A new value-added product (VAP)—Lifting Condensation Level Height (LCLHEIGHT)—computes LCL heights from continuous surface-air observations at the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) user facility’s Southern Great Plains (SGP) atmospheric observatory.
The LCL is the altitude at which a parcel of (moist) surface air becomes saturated while ascending dry-adiabatically.
LCLHEIGHT is used as input to the Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) ARM Symbiotic Simulation and Observation (LASSO) activity. Within LASSO, the LCL helps with identifying clouds coupled to the surface and evaluating the large-eddy simulation’s LCL height in the context of regional LCL variability.
The VAP computes LCL heights from continuous, 1-minute measurements of surface atmospheric state at 16 SGP facilities and 133 Oklahoma Mesonet environmental monitoring stations. LCLHEIGHT also includes the associated surface pressure, air temperature, and moisture content in the form of relative humidity.
LCLHEIGHT data from January 1, 2017, to December 30, 2019, are now available. The VAP will be run operationally on additional data as they become available.
More information on LCLHEIGHT can be found on the VAP web page. Feedback on the VAP can be sent to Tami Fairless.
Users can access the LCLHEIGHT data in the ARM Data Center. (Go here to create an account to download the data.)
To cite LCLHEIGHT data, please use doi:10.5439/1631820.
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















