Lagrangian Large-Scale Forcing Data Released for MOSAiC
Published: 24 October 2024
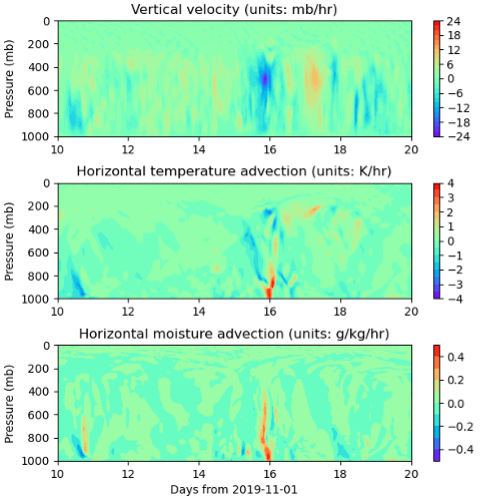
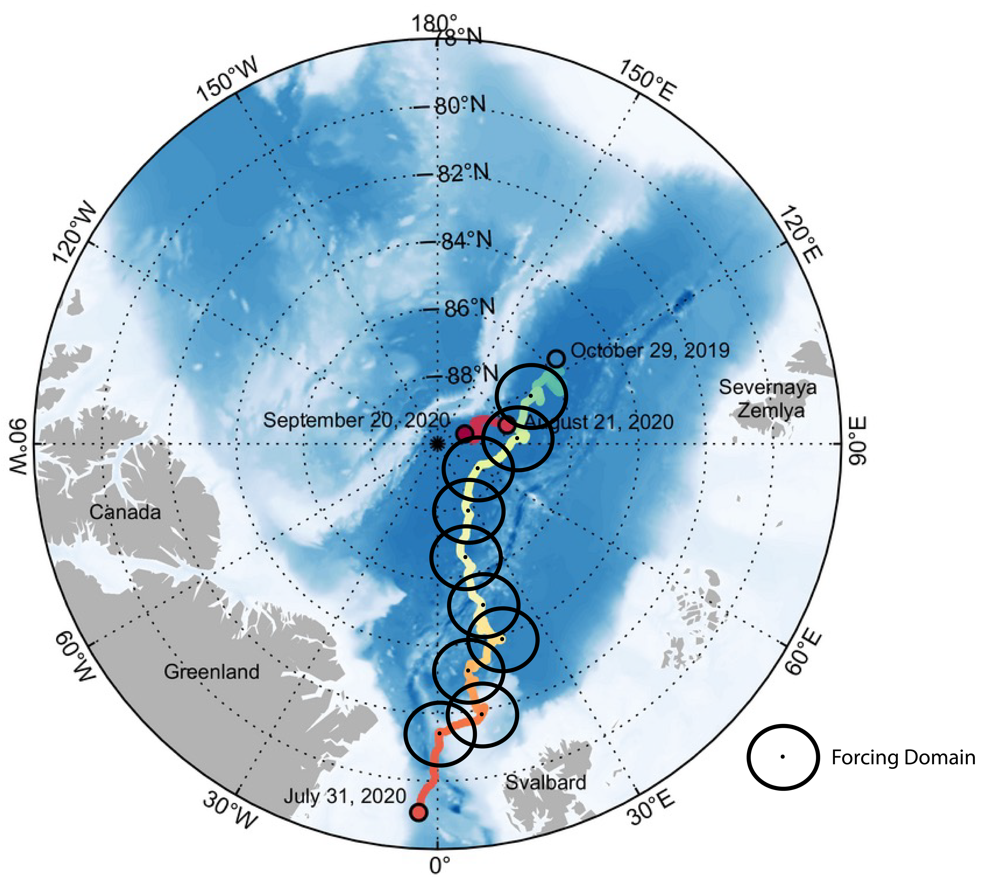
A new Lagrangian trajectory-based large-scale forcing data product from the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) user facility is now available for evaluation. The first data from this value-added product, known as ARMLAGTRAJ, are from November 2019 through January 2020 during the Multidisciplinary Drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate (MOSAiC) expedition. As part of the 13-month expedition, ARM operated more than 50 instruments on and around a research icebreaker frozen into drifting sea ice in the central Arctic.
Scientists can use ARMLAGTRAJ to drive single-column models, cloud-resolving models, and large-eddy simulation models in a Lagrangian framework, as well as to compare their simulation results of clouds and radiation with observations.
With some modifications that are described in the ARMLAGTRAJ technical report (Tao et al. 2024), the MOSAiC forcing data were produced using the Python-based lagtraj tool (Boeing et al. 2020), which generates forcings in Eulerian and Lagrangian modes using a fully automated framework. The data were generated in a Lagrangian framework, with the trajectory of the forcing domain following the movements of the ship-based observational platforms. These data are different from ARM’s variational analysis (VARANAL) large-scale forcing data, which represent domain averages at fixed locations.
ARMLAGTRAJ for MOSAiC was developed based on European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Reanalysis version 5 (ERA5) data. The forcing data represent an average over the 111-square-kilometer domain centered at ship locations. In addition to output variables derived from the ERA5 data using lagtraj (e.g., vertical velocity, horizontal/vertical temperature and moisture advection), variables from available ARM observations, such as column precipitable water, liquid water path, and surface downwelling and upwelling shortwave and longwave fluxes, are included for evaluation and comparison with the ERA5 data.
The data are provided as monthly files in netCDF format, with a time resolution of 60 minutes and a vertical resolution of 25 hPa.
Scientists can begin using the new MOSAiC large-scale forcing data for model simulation and evaluation of polar clouds in a Lagrangian framework.
Lagrangian large-scale forcing data for the Marine ARM GPCI Investigation of Clouds (MAGIC) is planned for fiscal year 2025. During MAGIC, ARM instruments collected data on a cargo ship that traveled back and forth between Los Angeles, California, and Honolulu, Hawaii, from October 2012 through September 2013.
More information about ARMLAGTRAJ can be found on the VAP web page.
To ask questions, report data issues, or provide feedback about the new VAP, please contact ARM VAP developer Cheng Tao or ARM translator Shaocheng Xie.
Access the ARMLAGTRAJ data in the ARM Data Center. (To download the data, first create an ARM account.)
To cite the ARMLAGTRAJ data, please use doi:10.5439/2376902.
References:
Tao C, M Zhang, and S Xie. 2024. Development of the ARM Lagrangian Large-Scale Forcing Data (ARMLAGTRAJ) Value-Added Product Based on the lagtraj Framework. Ed. by Robert Stafford, ARM user facility. DOE/SC-ARM-TR-306. https://doi.org/10.2172/2433924.
Boeing S, L Denby, PN Blossey, R Neggers, Z Cui, R Burton, and L Saffin. 2020. “Sensitivity of EUREC4A/ATOMIC LES to large-scale tendencies.” Presented at the 2020 American Geophysical Union (AGU) Fall Meeting, virtual.
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















